
Agile training is a form of education and professional development intervention focused on the Agile methodology and its principles, practices, and tools. The goal of Agile training is to help individuals and organizations understand and effectively implement the Agile ways of working.
There are many different types of Agile training programs available, ranging from introductory courses to Advanced certification programs. Agile Trainings can also be role based like scrum master /product owner or Development team focussed or framework based like Scrum, Kanban, SAFe etc.
Agile training can be delivered in a variety of formats, including in-person classes, online courses, and workshops. It is suitable for individuals and organizations of all sizes, and can be customized to meet the specific needs and goals of each participant.
The purpose of this blog is to understand in detail
- How to plan an Agile Training for maximum learning takeaway
- How to Identify the audience of agile training workshops
- Key Aspects of training like Interaction and gamification
- Ways to bring in simulation in the training workshop
- How to bring in Flavors of multiple frameworks in the training
How To Plan Your Agile Training
- How To Plan Your Agile Training
- Who are your Audience for Agile training and How to Identify them
- Why Are Cross Functional Teams Important in Agile trainings?
- Key Aspects of Developing Agile Training Plan
- Use Gamification for a better understanding of topics
- How to bring in Flavors of multiple frameworks in the training
- Steps for Scrum Simulation
- Things to Cover in Kanban Training
- Steps for Kanban Simulation
- Conclusion
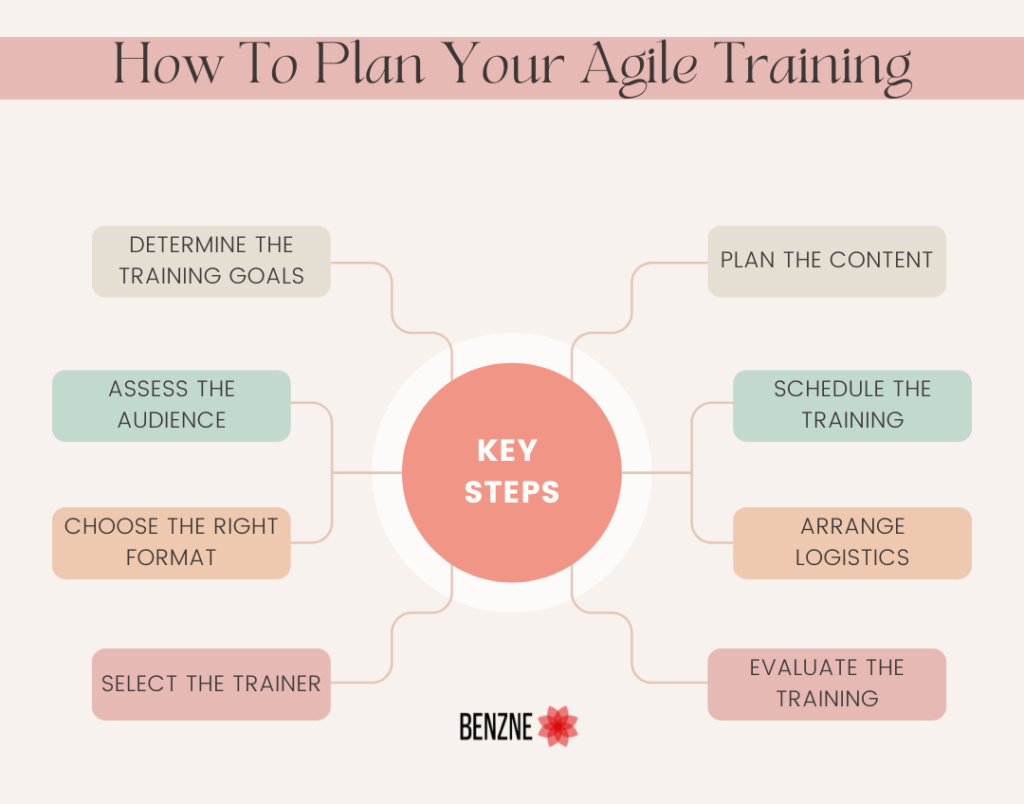
Planning an Agile training program requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure that the training is effective and meets the needs of the participants. Here are some steps to consider when planning an Agile training program:
- Determine the training goals: Clearly define the objectives of the training program and what the participants should be able to do after completing the program. This will help you determine the type and level of training that is needed.
- Assess the audience: Consider the backgrounds and experience levels of the participants to ensure that the training is appropriate for their needs. You may need to offer different levels of training for different groups of participants.
- Choose the right format: Decide on the format for the training, such as in-person classes, online courses, or workshops. Consider the preferences and needs of the participants, as well as the availability of trainers and resources.
- Select the trainer: Choose a trainer who has the appropriate experience and expertise to deliver the training. Consider their credentials, references, and any previous training experience.
- Plan the content: Develop a detailed training plan that covers all the topics and practices that the participants need to know. Ensure that the content is relevant, engaging, and appropriate for the audience.
- Schedule the training: Decide on a suitable time and location for the training. Consider the schedules and availability of the participants, as well as any logistical or resource constraints.
- Arrange logistics: Make arrangements for any necessary resources and materials, such as computers, projectors, or training aids. Consider any additional support or resources that may be needed for the participants, such as transportation or accommodation.
- Evaluate the training: Plan for evaluating the effectiveness of the training program. This may include assessments, surveys, or feedback sessions to help you understand how well the training was received and what can be improved.
Who are your Audience for Agile training and How to Identify them
Identifying the audience for an Agile training program is an important step in ensuring that the training is effective and meets the needs of the participants. Here are some steps to help you identify the audience for an Agile training program:
- Understand what is the need for the training workshop: Start by defining the objectives of the training program and what the participants should be able to do after completing the program. This will help you determine the type and level of training that is needed.
- Assess if it is a specific or a general Training: Consider the current state of the organization and the specific Agile practices and principles that need to be addressed. This will help you determine who needs to attend the training and what their specific needs and goals are.
- Identify key stakeholders: Determine who in the organization will be affected by the adoption of Agile and who needs to be involved in the training. This may include managers, team leaders, developers, and other key stakeholders.
- Consider experience levels: Consider the backgrounds and experience levels of the participants to ensure that the training is appropriate for their needs. You may need to offer different levels of training for different groups of participants.
- Determine the size of the audience: Consider the number of participants who will attend the training and whether the training format can accommodate the size of the audience.
Gain insights into agile methodologies with consulting agile services. Empower your team for successful agile adoption. Explore our solutions now.
Why Are Cross Functional Teams Important in Agile trainings?
Cross-functional teams play an important role in Agile training as they can provide a diverse range of perspectives and skills that are necessary for successful Agile implementation. In a cross-functional team, members from different departments or functional areas work together to achieve common goals.
In the context of Agile training, a cross-functional team may include members from development, project management, product management, quality assurance, and other relevant functional areas. This diversity of perspectives and skills can help to ensure that the training is relevant and effective for all members of the team.

Here are some benefits of using cross-functional teams for Agile training:
- Improved collaboration: Cross-functional teams can encourage collaboration and communication among members, which is critical for successful Agile implementation.
- Increased understanding: Members from different functional areas can bring different perspectives and experiences to the training, which can lead to a deeper understanding of Agile principles and practices.
- Better alignment: Cross-functional teams can help to ensure that all members of the organization are aligned with the Agile approach and are working towards common goals.
- Improved outcomes: Cross-functional teams can lead to better outcomes as they can leverage the skills and perspectives of members from different functional areas to solve complex problems and achieve common goals.
Key Aspects of Developing Agile Training Plan
Making it more Interactive
By encouraging interaction during Agile training, you can promote a deeper understanding of the material, build a sense of community among participants, and ensure that the training is effective and meets the needs of the participants. Here are some ways to encourage interaction during Agile training:
- Active participation: Encourage participants to actively participate in the training, rather than just passively listening to the trainer. This can include group discussions, case studies, role-playing exercises, and other interactive activities.
- Collaborative activities: Encourage collaboration among participants through group activities, such as team-building exercises or working on a common project. This can help to build a sense of community and encourage participants to work together more effectively.
- Q&A sessions: Provide opportunities for participants to ask questions and engage in discussion with the trainer and other participants. This can help to clarify any misunderstandings and promote a deeper understanding of the material.
- Feedback loops: Encourage participants to provide feedback on the training, such as what they found helpful or what could be improved. This can help to ensure that the training is effective and meets the needs of the participants.
- Real-world examples: Use real-world examples and case studies to illustrate the concepts and practices being covered in the training. This can help to make the material more relevant and engaging for the participants.
- Use Anecdotes : Certain topics may be tough to explain or even understand. In these case use Anecdotes to relate the topic to make the participants understand better
- Usage of Tools : Use tools like Mural, Mentimeter, EazyRetro etc where the participants can also input their thoughts and interact more
Use Gamification for a better understanding of topics
By incorporating gamification into Agile training, you can make the training more engaging and interactive for participants, promote a deeper understanding of Agile principles and practices, and help to reinforce learning.
Here are some ways to incorporate gamification into Agile training:
- Points system: Award participants with points for completing tasks or demonstrating their understanding of Agile concepts and practices. This can help to motivate participants and encourage them to engage more fully with the training.
- Quizzes and challenges: Use quizzes, challenges, and other interactive activities to test participants’ knowledge and understanding of Agile principles and practices. This can help to reinforce learning and make the training more engaging.
- Simulation games: Use simulation games to help participants apply Agile concepts and practices in a real-world context. This can help to make the material more relevant and engaging for participants.
- Role-playing exercises: Encourage participants to role-play scenarios related to Agile practices and principles. This can help to build empathy and understanding among participants and make the training more engaging.
- Leaderboards: Use leaderboards to encourage friendly competition among participants and create a sense of accomplishment. This can help to motivate participants and encourage them to engage more fully with the training.
How to bring in Flavors of multiple frameworks in the training
Things to Cover in a Scrum Training
Here are some important topics to cover in Scrum training:
- Introduction to Agile and Scrum: Provide a comprehensive overview of Agile, including its values, principles, and methodologies, and the specific role that Scrum plays within the Agile framework.
- Scrum Process: Explain the Scrum process, including the Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, Sprint Retrospective, and Backlog Refinement events.
- Scrum Roles: Discuss the different roles in Scrum, including the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team, and their responsibilities.
- Scrum Artifacts: Explain the purpose and use of the main Scrum artifacts, such as the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, Increment, and Burn-down chart.
- Scrum Techniques: Discuss the various techniques used in Scrum, including User Stories, Estimation and Planning with Story Points, Task Boards, and Definition of Ready.
- Case Studies: Provide case studies and examples of successful Scrum implementations to help participants see how Scrum is being used in real-world situations.
- Best Practices for Implementing Scrum: Discuss best practices for implementing Scrum in an organization, including tips for overcoming common challenges.
Steps for Scrum Simulation
Simulating a Scrum sprint in Agile training can be a useful way to help participants understand and apply Scrum principles and practices in a real-world context. Here are some steps to simulate a Scrum sprint in an Agile training:
- Form teams: Participants should be divided into small, cross-functional teams of 5-9 people.
- Assign roles: Each team should assign roles such as Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team members.
- Identify a project: The teams should identify a project they would like to work on, such as creating a new product or improving an existing one.
- Plan the sprint: Each team should plan the sprint, including defining the Sprint Goal, breaking down the project into smaller tasks, and estimating the effort required to complete each task.
- Conduct the sprint Planning: The teams should then hold the sprint, working through each task and updating the Sprint Backlog as needed.
- Conduct daily stand-ups: Each team should hold daily stand-ups, where team members report on their progress and any obstacles they are facing.
- Conduct the Sprint Review: At the end of the sprint, each team should hold a Sprint Review, where they demonstrate what they have completed and receive feedback from other participants.
- Conduct the Sprint Retrospective: After the Sprint Review, each team should hold a Sprint Retrospective, where they reflect on what went well and what could be improved in the next sprint.

Things to Cover in Kanban Training
Here are some important topics to cover in a Kanban training:
- Introduction to Kanban: Provide an overview of Kanban, its history and evolution, and its core principles and values.
- Visualizing Work: Discuss the importance of visualizing work in Kanban and explain how to create a Kanban board and use it to manage work items.
- Managing Workflow: Explain how to manage workflow in Kanban, including how to prioritize work, manage flow, and limit work in progress.
- Managing Queues: Discuss the different types of queues in Kanban, including input, work, and output queues, and explain how to manage and optimize them.
- Lead Time and Cycle Time: Explain the difference between lead time and cycle time and discuss how to measure and optimize these metrics in Kanban.
- Policies and Procedures: Discuss the policies and procedures used in Kanban, including how to manage pull-based flow, how to implement continuous improvement, and how to handle blockers and interruptions.
- Measuring and Improving Performance: Explain how to measure and improve performance in Kanban, including how to use metrics such as cumulative flow diagrams, control charts, and histograms.
- Integrating Kanban with other methodologies: Discuss how Kanban can be integrated with other Agile methodologies, such as Scrum, and how to use Kanban as a complement to other approaches.
- Case Studies and Best Practices: Provide case studies and best practices to help participants see how Kanban is being used in real-world situations, and to learn from the experiences of others.
Steps for Kanban Simulation
Here are the steps for conducting a Kanban simulation:
- Prepare the materials: Gather all the materials you will need for the simulation, including sticky notes, markers, a whiteboard or flip chart, and any props that you think will be helpful.
- Explain the simulation: Give the participants a brief overview of the simulation and its objectives, and explain how it will be conducted.
- Set up the Kanban board: Draw a simple Kanban board on the whiteboard or flip chart, including columns for To Do, In Progress, and Done.
- Create work items: Write work items on sticky notes, and place them in the To Do column of the Kanban board.
- Start the simulation: Explain the rules of the simulation, such as how work items will be pulled from one column to the next, how work in progress will be limited, and how work items will be completed.
- Facilitate the simulation: Encourage participants to work together to move work items through the Kanban board, and help to resolve any challenges or obstacles that arise.
- Evaluate the simulation: After the simulation is complete, discuss the results with the participants and evaluate how well the simulation met its objectives.
- Reflect on the experience: Encourage participants to reflect on the experience and discuss what they learned about Kanban, including its strengths and weaknesses, and how it can be used in their own work.
Recommended Read
Conclusion
With this, our blog “What should the learning team keep in mind while planning Agile Training?” comes to an end. Please note that any agile transformation journey follows a know-do-be Agile cycle. A good agile training serves as a solid foundation for participants to understand the basic practices and use cases. Your teams may still need help and guidance as they start implementing agile ways of working in their jobs.
We really hope this is of help. In case of any feedback or suggestions, please reach out to us at consult@benzne.com


One Reply to “How To Develop Agile Training Plan”