Introduction to Agile Implementation Challenges
In today’s fast changing environment of software development, Agile has become the go to mode of working to be more flexible, efficient, and improve continuously. With its benefits of delivering quality products faster and adapting to changing requirements, most of the organizations have moved towards agile ways of working .
Being Agile and reaping the benefits of agility requires a change of mindset, process and culture. Agility is definitely not achieved in 2-3 weeks but is a journey teams take to change their ways of working over a long period of time. We need to identify the transformation phases, develop a transformation plan and coach teams to implement agile ways of working to align with the goals of the transformation.
Implementing Agile involves not only adopting new processes and practices but also fostering a cultural shift within the organization. This includes changing mindsets, encouraging collaboration, and embracing a more adaptive and responsive approach to deliver a product. It is a given that there would be roadblocks and challenges when there is a change introduced in the system and it may become chaotic if they are not addressed. Even a seasoned agile practitioner may come across some commonly faced problems like:
- Resistance to change
- Insufficient stakeholder engagement
- Misaligned goals
- Inadequate awareness
This blog aims at exploring some common agile implementation challenges and how to address them including:
- Why and where do the agile transformations fail?
- What are the common causes of agile implementation failures?
- What are a few common agile implementation challenges?
- How do we ensure the agile transformation goals are met?
- How can you overcome agile adoption challenges?
- What are the key barriers to agile adoption?
- What are the common agile implementation problems?
- What are the key issues in implementation of agile?
What is agile Implementation?
Agile implementation refers to the process of adopting and integrating Agile methodologies into an organization or project. Agile is a set of principles and practices aimed at improving flexibility, collaboration, and customer-centricity in the development of products, particularly in software development. The implementation of Agile involves transitioning from traditional, often rigid, project management and development approaches (such as Waterfall) to more iterative and incremental methods. 4 main pillars of agile implementation asks for:
- Cultural Change: Encouraging a mindset that values collaboration, transparency, and continuous improvement.
- Process Change: Implementing Agile frameworks like Scrum or Kanban to guide work processes.
- Structural Change: Creating cross-functional teams that can work independently and have all the necessary skills to complete a project.
- Leadership style Change: Shifting from a command-and-control style of management to one that supports and empowers teams.
Common Causes of Agile Implementation Failures
Agile implementation can be challenging, and several common factors can lead to its failure. Understanding these potential agile adoption challenges and failures can help organizations better prepare and avoid common mistakes. It is imperative that any organizations will face issues in implementation of agile as it is disrupting an existing process and way of working. Here are some common causes of Agile implementation failures:
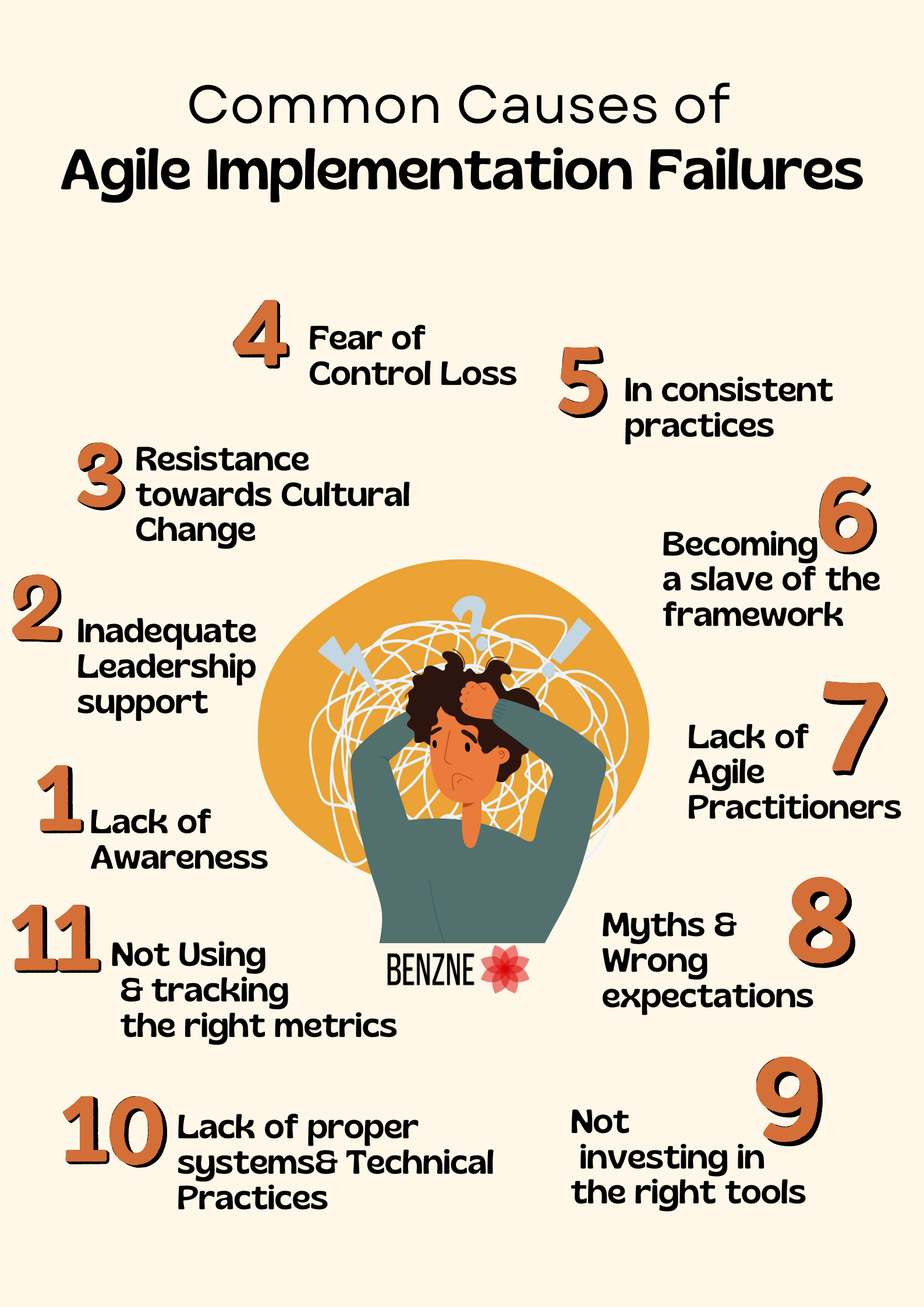
- Lack of Awareness – Team members and leaders may not fully understand Agile principles and practices, leading to improper implementation
- Inadequate Leadership support – Without strong commitment and support from leadership, Agile initiatives may struggle to gain traction or to cross pollinate
- Resistance towards Cultural Change – Existing organizational culture may resist the transparency, collaboration, and flexibility required by Agile
- Fear of Control Loss – Managers and team members may fear losing control or authority in a more self-organizing Agile environment
- In consistent practices – Not adhering consistently to Agile ceremonies, roles, and artifacts can undermine the process
- Becoming a slave of the framework – Using Agile frameworks (like Scrum or Kanban) incorrectly or without adaptation to the organization’s context can lead to inefficiencies
- Lack of Agile Practitioners – Without experienced Agile coaches, teams may struggle to navigate challenges and adapt practices effectively
- Myths and Wrong expectations – Expecting rapid results without allowing time for adaptation and learning can set teams up for failure
- Not investing in the right tools – Inadequate tools for collaboration, tracking, and continuous integration can hinder Agile processes
- Lack of proper systems and Technical Practices – Issues like poor code quality, lack of automated testing, and ineffective DevOps practices can disrupt Agile workflows
- Not Using and tracking the right metrics – Using traditional metrics that don’t align with Agile values (e.g., focusing on output rather than outcomes) can skew priorities and behaviors
Key Agile Implementation Challenges
Agile helps businesses or organizations in a lot of ways. Agile implementation requires change in people, process and leadership thought process. However, there are also a set of challenges in the agile implementation journey. Some of the common agile implementation problems in organizations include:

Unrealistic expectations and overemphasis on Agile outcomes
One of the common agile adoption challenges is the presence of unrealistic expectations and an overemphasis on Agile outcomes. These issues can lead to disappointment, misalignment, and failure to realize the true benefits of Agile methodologies. Some key aspects of these challenges are:
- Expecting immediate results after implementing one of the agile frameworks
- Expecting SCRUM to solve all agile problems
- Looking for precise and concrete plans and timelines for the project
- Ignoring the fact that cultural changes may require some time
- Expecting agile to solve all the problems
Resistance to change
Resistance to change is another common challenge in implementing agile. It happens when individuals or teams within an organization resist modifications to set processes, systems, or behaviors. Below are a few causes which may cause the resistance:
- Fear of Unknown and uncertainties in the new roles and responsibilities
- Agile can be looked as a threat to managers who are more control focussed
- Need to maintain the status quo and being reluctant towards change
- Ghost of the past may also promote resistance towards agile implementation
- Lack of awareness causes panic and chaos within the teams and individuals
Lingering traces of traditional methodologies
When an organization moves towards Agile methodologies, it often comes across lingering traces of traditional methodologies such as Waterfall or other plan-driven approaches. These can be in processes, mindsets, and practices, potentially hindering the full realization of Agile benefits. Some of these practices which increases agile implementation difficulties include:
- Detailed requirements and planning
- Silo set up of work environments
- Handoffs and overheads because of org structure
- Detailed documentation and sign offs
- Scope creep fear
Excessive focus on artifacts over Agile principles
In Agile, artifacts are important tools that ensure transparency, communication, and progress tracking. However, only focussing on these artifacts can dilute the core Agile principles and values, leading to a surface level implementation that misses the actual benefits of Agile.
One of the best examples is how teams run to achieve a particular velocity. Velocity chart is to understand the gaps in the process in terms of how the team is planning and completing their sprint increments. But most of the teams tend to achieve a target velocity as set by their managers.
Lack of talent investment
Agile is the most flexible ways of working for the current every changing world. There are new tech stacks, languages, systems, design patterns emerging frequently and continuously. Failing to invest in talent can significantly hinder the success of Agile transformation. Some of the aspects of lack of talent investment include:
- Trainings and cross pollination of knowledge on agile, technical innovation
- Limited time and resources for skills development
- Inadequate hand holding by subject matter experts
- Lack of support for continuous learning
Absence of a long-term vision
Agile is all about moving continuously towards the right direction. Another main agile implementation challenge is the absence of a long-term vision. While Agile methodologies promotes flexibility and responsiveness to change, they also require a clear, long-term vision to provide direction to the teams and the organization. These are a few symptoms of what happens when teams lack direction:
- Teams and individuals focussing on getting tasks done without knowing the big picture
- Different teams and groups focussing on different goals
- No clear basis for prioritization
- Not being able to take decisions
- Difficulty in scaling agile framework and structuring
Neglecting iteration and experimentation
Agile is about iteration and experimentation that drive continuous improvement, innovation, and responding to change. However, neglecting these aspects can hinder the effectiveness of Agile practices and limit a team’s ability to respond to changing requirements and market conditions. Neglecting iteration is another barrier to agile adoption and can surface in several ways, from following a concrete plan to a lack of risk-taking and innovation. But how do teams neglect iteration and innovation? Here are a few examples:
- Sticking to a concrete plan and not being able to pivot
- Failure being discouraged
- Running behind delivery and lack of time for innovation
- Not much feedback loops
- No awareness of MVP and prototyping concepts
Challenges in evaluating Agile success
Evaluating the success of Agile implementations can be challenging due to the unique nature of Agile methodologies, which mainly is about flexibility, customer collaboration, and continuous improvement over traditional metrics and processes. With different orgs having different understanding and purpose of agile, here are a few challenges that surfaces up when it comes to evaluating agile success:
- Different teams may define success differently
- Misunderstanding with metrics (Velocity defines success)
- Systems and tools needed to measure success (CSAT, NPS etc)
- No harmony in agile adoption
Difficulty in communicating Agile to customers
Communicating Agile methodologies and principles to customers can be challenging, especially when customers are used to more conventional project management approaches like Waterfall. Agile’s iterative nature, focus on flexibility, and emphasis on customer collaboration can sometimes be misunderstood or seem confusing to clients who expect fixed timelines and detailed planning at the beginning. Here are a few common challenges teams face in communicating agile to customers:
- Customers may expect detailed project plans with fixed scope, deadlines, and costs
- Terms like “sprints,” “backlogs,” “user stories,” and “iterations” may be unfamiliar or unclear to customers, making it hard for them to understand the process
- Traditional approaches that often have detailed Gantt charts and milestone-based tracking, Agile’s focus on working increments can make it harder for customers to visualize progress
- Customers may struggle to see the value of iterative delivery, especially if they are used to receiving a final, complete product at the end of a project
Insufficient organizational buy-in
Not everyone in the company may support or believe in the change to Agile methodologies. This lack of support can come from various levels, including leadership, management, or team members, and can become an agile implementation challenge. When there isn’t enough buy-in, it can lead to resistance, inconsistent practices, and difficulty in achieving the benefits of Agile. Simply put, it’s like trying to move forward with a plan when not everyone is on board with the idea.
Resistance from change-resistant individuals
Individuals may get stuck with familiar routines and processes, find it hard to adjust to new practices, or fear the uncertainties that change can bring. Their resistance can slow down or complicate the transition to Agile, making it more challenging to achieve the desired improvements and benefits. Essentially, it’s when people are uncomfortable with the changes being introduced, often because they are used to doing things the old way or their bad experiences from the past. But here is how it may become a challenge:
- Change-resistant individuals may delay the adoption of Agile practices
- Resistance can create tension and conflict within teams
- If everyone in the teams are not supportive the effectiveness of the transformation becomes less
Lack of transparent communication
For Agile transformation to be successful, it’s vital that everyone involved understands the vision, goals, and processes. Transparent communication helps in building trust, ensuring alignment, and fostering a culture where team members feel valued and included. When there is no clear and transparent communication, we could face a lot of problems like:
- Team members and stakeholders may not understand what’s happening, why changes are being made, or what is expected of them and lead to chaos
- Lack of openness can lead to reduced trust in leadership and the change process
- People may feel disconnected if they aren’t kept informed
Excessive risk aversion
Taking risks is one of the key aspects which promotes innovation and continuous improvement. Not being able to take risks or working in a risk free environment may reduce the opportunities where teams can try new initiatives. This mindset can significantly block the Agile process, which emphasizes experimentation, learning from failures, and iterating based on feedback.
Some of the common pitfalls include:
- Fear of trying new practices
- Experimenting with innovative ideas
- Making changes to established processes
Preservation of legacy control mechanisms
The legacy mechanisms often include rigid processes, extensive documentation requirements, strict approval chains, and heavy reliance on hierarchical decision-making. While these practices may have been effective in more traditional project management environments, they can conflict with Agile principles, which emphasize flexibility, empowerment, and continuous delivery of value. Here are some pointers on what happens with legacy mechanisms:
- Delayed decision making
- Teams not having enough autonomy
- Increased focus on formal reporting and documentation
- Lack of opportunities for innovation
Premature scaling attempts
When it comes to scaling agile, the first thing to ensure is that the individual teams have adequate agile maturity, there might be a need to synchronize the cadences, and bring a common harmony within teams in understanding of agile practices. If these aspects are not taken care of, there could be all possibility of the scaling approach going chaotic. Some issues which may come up during scaling:
- No consistency in agile practices
- Different teams with different levels of agile maturity
- No harmony in tools being used and metrics being monitored
- Communication challenges
- Dependency management
Inappropriate standardization efforts
Imposing uniform processes, practices, or tools across all agile teams in an organization, without taking into account the unique needs, contexts, and maturity levels of those teams could become a major agile adoption challenge. While some level of standardization can provide consistency and facilitate coordination, overly rigid or inappropriate standardization can undermine the flexibility and adaptability that are core to Agile methodologies.
Misalignment with core Agile values
Misalignment with core Agile values happens when the practices, policies, or culture of an organization conflict with the fundamental principles and values outlined in the Agile Manifesto. Agile values emphasize individuals and interactions, working software, customer collaboration, and responding to change. When there is a misalignment, the true benefits of Agile may not be realized, and the implementation can fail to achieve its intended outcomes.
Inadequate experience with Agile
Lack of sufficient knowledge or practical experience in implementing Agile methodologies, which can hinder the successful adoption and execution of Agile practices within an organization. This can occur at various levels, from individual team members to leadership, and can impact the overall effectiveness of Agile initiatives. Below are a few symptoms of inexperience with agile:
- Not understanding / digesting the agile principles
- Partial implementation based on old experience or individual understanding
- No Subject matter expertise to mentor teams
- Limited systems and tools to support continuous improvement
- Lack of ability to address challenges
Lack of management support
One of the vital parts of a successful agile transformation is the support from management. Insufficient backing, encouragement, and commitment from leadership and management for Agile initiatives within an organization could very much become one of the challenges in agile project management. Below are a few symptoms where this can be observed clearly:
- Limited or lack of resources
- Not prioritizing agile initiatives
- Not funding agile projects
- Inadequate coaching and training
- Lack of authority to promote agility
External pressure to adhere to legacy systems
External pressure to adhere to legacy systems means facing demands or expectations from outside the organization to stick with old, conventional systems and processes, rather than adopting new, more efficient ones. Here are a few factors which can influence this:
- Regulatory requirements
- Customer being adamant
- Legacy vendors
- Integration challenges
How can you overcome agile adoption challenges?
The section above gives us a picture of challenges in implementing agile. However, there are ways to address these challenges to ensure teams and organizations become agile and make it a success, let’s explore how.
- Provide training for all levels, from team members to management, to ensure everyone understands Agile principles, practices, and their roles in the process
- Promote certifications (like Scrum Master or Product Owner) and participate in Agile workshops to deepen understanding and skills
- Gain trust from leadership team who can act as a catalyst in Agile initiatives, allocate resources, and drive cultural change
- Promote a leadership style that supports autonomy and decision-making
- Maintain open and honest communication across all levels of the organization to foster trust and align on goals
- Use daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives to facilitate communication, address issues, and continuously improve
- Set up an environment for experimentation, learning from failures, and celebrating successes. This helps teams adapt and evolve their practices
- Implement regular feedback loops with stakeholders, customers, and within teams
- Customize Agile practices to fit the unique context of your organization and teams
- Start with small projects or pilot teams to test and refine Agile practices before scaling up
- Use best fit project management and collaboration tools to support Agile practices, such as Jira, Trello, or Azure DevOps
- Establish metrics that align with Agile principles, such as customer satisfaction, time-to-market, and quality improvements, rather than just velocity
- Involve individuals in the process, get their input, and make them a part of the change
- Encourage the formation of cross-functional teams that bring diverse skills and perspectives to solve problems
How do Consulting Agencies Aid Businesses in Overcoming Agile Implementation Challenges?
Agile management consulting companies like Benzne play an important role in helping companies adopt agile ways of working. Consultants are subject matter experts and generally come with a lot of ground level experience and are unbiased in their implementation approach. Here are a few pointers on how consulting firms can help in overcoming challenges in implementing agile:
- As Is Assessment and Strategic Roadmapping – Agile consulting firms start their implementation journey with an assessment to understand the current team’s maturity and practices. Based on the assessment, they create a tailored customized roadmap to align with the problem statement or goals
- Framework Agnostic, Outcome Driven Transformation – Consultants are SMEs who have knowledge of various frameworks. They design and recommend framework implementation based on need rather than just applying one framework because of organizational norms. They cater to solving a problem with best suited framework with agility in mind versus adopting agile for the sake of it
- Education/Awareness and Education – Consulting firms provide training and programs to train teams and stakeholders with Agile principles, practices, and frameworks such as Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming (XP). Training sessions may include workshops, seminars, and hands-on exercises to reinforce learning based on the need
- Coaching and Handholding – Agile consultants work closely with teams and leadership to guide them through the Agile transformation process. They provide ongoing support, feedback, and guidance on implementing Agile practices, resolving challenges, and adapting to change.
- Unbiased, Outside-In Perspective – Consultants are generally contract based and the contracts are usually outcome driven. Their experience having worked with multiple companies enables them to overcome challenges/resistance with a lot more ease and help organizations with insights with their experience.
- Metrics and Milestone Based Transformations – Consultants contracts are usually for a shooter duration and outcome driven. And usually there are intermediate milestones and KPIs based on the roadmap more like a checkpoint. This enables the companies agile transformation to be more fast and effective.
Conclusion
Agile is a set of principles and practices aimed at improving flexibility, collaboration, and customer-centricity in the development of products, particularly in software development. The implementation of Agile involves transitioning from traditional, often rigid, project management and development approaches (such as Waterfall) to more iterative and incremental methods.
While the journey can be exciting, it can also come up with a lot of practical challenges. From cultural resistance and misalignment with Agile values to the technical complexities of integrating new tools and processes, the challenges in implementing agile can become endless leading to a failure and eventually to a state where people lose hopes on Agile.
It becomes very crucial to understand the symptoms of antipatterns, to quickly create a success story and then to cross pollinate. Key to overcoming these challenges is an approach that includes good training, strong leadership support, effective communication, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Ultimately, the success of Agile implementation depends on the need of the entire organization to embrace change, experiment with new approaches, and learn from both successes and failures.
It is important to understand that it is not just about adopting a new methodology—it’s about transforming the way your organization thinks, collaborates, and delivers value. With the right mindset and strategies, Agile can become a powerful catalyst for achieving your business goals.
With this, our blog on “Benzne Blog – Agile Implementation Challenges: A Roadmap to Success” comes to an end we hope this has helped you understand and tackle your transformation challenges. Please write to “consult@benzne.com” for any feedback or suggestions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Agile Implementation Challenges
1.What is the roadmap in the Agile implementation process?
The agile implementation process involves several key steps and practices aimed at adopting Agile methodologies effectively within an organization. These Steps include:
- As Is understanding of the current state
- Getting leadership and stakeholders buy in
- Selecting a few pilot projects to start with
- Selecting a framework to implement
- Educating the team members on the framework
- Create the backlog
- Implement the iterative and incremental process
- Measure the progress
- Introduce best practices
- Continuously improve based on feedback
2.Which two are common challenges faced by organizations during Agile implementation?
The two most common agile implementation challenges which teams face during agile implementation are:
- Resistance to Change – Resistance to change is one of the common challenges in implementing agile. It happens when individuals or teams within an organization resist modifications to set processes, systems, or behaviors. Below are a few causes which may cause the resistance:
- Fear of Unknown and uncertainties in the new roles and responsibilities
- Agile can be looked as a threat to managers who are more control focussed
- Need to maintain the status quo and being reluctant towards change
- Ghost of the past may also promote resistance towards agile implementation
- Lack of awareness causes panic and chaos within the teams and individuals
- Misalignment with core agile values – Misalignment with core Agile values happens when the practices, policies, or culture of an organization conflict with the fundamental principles and values outlined in the Agile Manifesto. Agile values emphasize individuals and interactions, working software, customer collaboration, and responding to change. When there is a misalignment, the true benefits of Agile may not be realized,and the implementation can fail to achieve its intended outcomes.
3.What is one practical problem of agile methods?
One of the common agile adoption challenges is the presence of unrealistic expectations and an overemphasis on Agile outcomes. These issues can lead to disappointment, misalignment, and failure to realize the true benefits of Agile methodologies. Some key agile implementation difficulties are:
- Expecting immediate results after implementing one of the agile frameworks
- Expecting SCRUM to solve all agile problems
- Looking for precise and concrete plans and timelines for the project
- Ignoring the fact that cultural changes may require some time
- Expecting agile to solve all the problems
4.What is the largest obstacle to the team being more Agile?
When an organization moves towards Agile methodologies, it often comes across traces of traditional methodologies such as Waterfall or other plan-driven approaches. These can be in processes, mindsets, and practices, potentially hindering the full realization of Agile benefits. Some of the barriers to agile adoption include:
- Detailed requirements and planning
- Silo set up of work environments
- Handoffs and overheads because of org structure
- Detailed documentation and sign offs
5.What are logical dependencies?
Logical dependencies, also known as logical relationships or task dependencies, refer to the connections between tasks or activities in a project that determine the sequence in which they must be performed. These dependencies indicate that one task relies on the completion or initiation of another task to proceed.
Advance your organization’s innovation journey with our agile innovation consulting. We turn ideas into actionable solutions, driving market leadership and sustainable growth in your sector.

I really like the way the challenges to agile transformation have been mentioned here. Yes I see these coming up over and over again,making life of the entire team more miserable and achieving goals as impossible because the teams don’t progress in either ways – Waterfall or Agile.Specially Project managers being called up as Scrum Masters when teams have been tuned to get organized tasks from a traditional project manager.Thanks for sharing this