Introduction
In today’s VUCA world where innovation is the key to drive success, traditional/conventional ways of problem solving may not be sufficient or even outdated. We need a framework that is iterative in nature, can bring in elements of empathy, collaboration to get multiple solutions, and then roll out the best solution based on the feedback. This may not be a prescriptive solution rather is a way of working or mindset shift that is needed.
But what teams or individuals keep in mind with respect to the construct or thought process is defined by the principles of design thinking. What guides the teams to explore problems, come up with perspectives, experiment and empathise with the users are the principles. Be it a fresher, management grade person or even a CEO, these principles should help teams or individuals with the right mindset to drive innovation and solve user centric problems to stay relevant.
This blog aims at guiding teams and individuals in understanding:
- What exactly is design thinking?
- What are the key principles of design thinking?
- How can we apply design thinking in our environment?
- What are the core principles of design thinking?
- What are some design thinking principles examples?
What is design thinking?
Design thinking is a simple yet powerful way of working that focuses on understanding the customer needs and developing innovative solutions. It promotes empathy, collaboration and experimentation to create human centered, consumer centric solutions.
Design thinking flow spreads across five stages:
- Empathize with the users – Putting yourself in the end user’s shoes to understand their problems, challenges and pain points
- Define the problem – Clearly define the problem you want to solve
- Ideate Potential solutions – Come up with different multiple solutions for the same problem
- Prototype – Create simple versions of your solution to test
- Test – Take your solutions to the end users to get feedback and build on top of it
These stages may not be sequential, that is there could be a lot of to and fro between these stages to come up with the best solution that solves the end user problems.
Key Design Thinking Principles
Design thinking principles are the guide that paves the path towards innovative solutions that are human centered. Before we jump into design thinking principles, let’s quickly understand the stages involved:
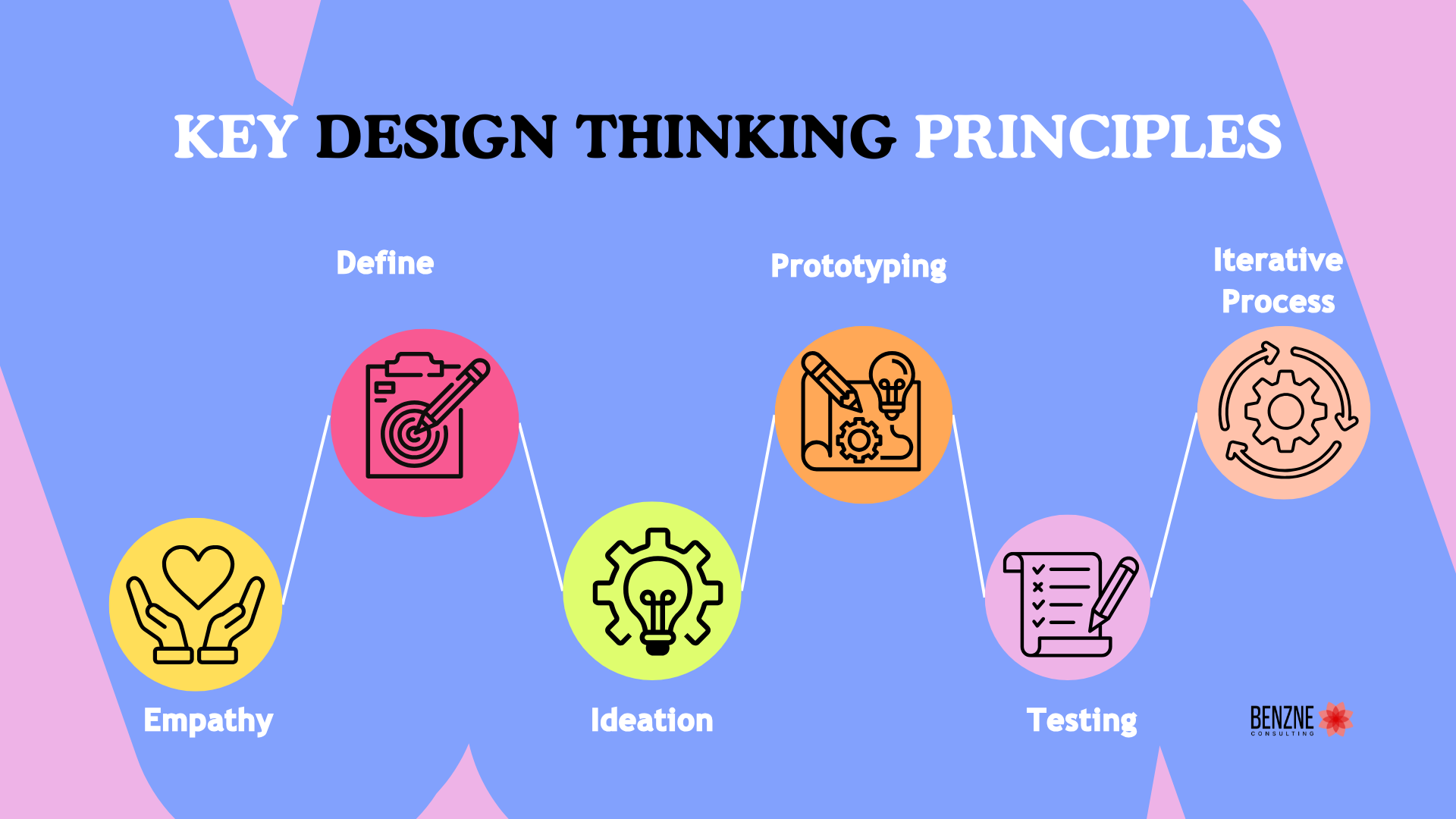
- Empathy: This stage is about understanding user needs and experiences and needs a good amount of observation, interviewing and also interaction with them. This creates an environment where we can understand who are the users, their challenges and pain points
- Define: This stage involves clearly writing down the specific problem the users are facing based on the insights gathered in the empathy phase. Writing down the specific problems helps teams to concentrate on solving the problem without any assumptions
- Ideation: This stage is about coming up with multiple solutions from multiple perspectives for a single problem. This removes any assumptions and promotes options by brainstorming the solutions
- Prototyping: With the best potential solution, the next stage is to quickly create a simple version of the solution like flow, visual designs wireframes that can help us validate if the solution we are thinking will actually solve the problem
- Testing: Users are at the center of design thinking. This phase involves taking the prototype to the set of actual users to test and validate the effectiveness of the solution
- Iterative Process: Is about repeating the phases in cycles as new problems and ideas come up. This helps in continuously improving and adapting. The main idea is on being flexible and learning from failure to arrive at the best potential solution
Design Thinking is built on some core principles that guide innovation and problem solving. With these principles, teams can develop user centered solutions that deliver impact which matters to the users and drive creativity. Let’s delve into the key principles of design thinking in detail:
Collaborative Approach
The most important design thinking principle is to collaborate. Collaboration brings in different perspectives from different people. It promotes open discussion and disagreements and diverse ideas among the teams that could potentially bring out a well rounded approach to problem solving. Collaboration helps teams to build on each other’s ideas and create innovative solutions that actually address the user needs.
Iterative Process
Design thinking is not a one time activity. It is an iterative process where all the stages mentioned above run in loops/cycles. This approach helps teams to learn from the mistakes and pivot quickly to make the solutions better. Iteration also reduces the risk blast radius by helping teams refine ideas continuously rather than making a perfect product at once.
Bias Towards Action
Rather than spending a lot of time on planning everything or sitting on a problem, design thinking promotes on quickly getting a prototype and taking it to the users, to get feedback. This helps teams in learning quickly and pivot or adjust their solution or approach based on insights from the users that really matter.
Mindset of Optimism
Design thinking helps us believe that even for a tough problem, there can always be a creative solution. It promotes a positive attitude to look at challenges as opportunities and approach them with an open mind. Because of the iterative nature, it brings in the flexibility as well to encourage teams to solve problems with an open mind.
Embrace Ambiguity
Teams may not understand the problem completely or even come up with a complete solution. Design thinking promotes a safe and comfortable environment to embrace uncertainty with an experimentation mindset. Especially in the ideate phase, teams explore different solutions with different perspectives and probe others with questions like “what if”, “why this”, “Why not?” and are open to new answers which may not have been thought of.
Focus on the Solution, Not Blame
The main idea of design thinking is to solve the problem. And it heavily depends on collaboration. When there is collaboration, the success of failure is not on one person but the entire team. This fosters a safe environment for the team members to share their opinions, challenge others, experiment , take risks and learn from failures.
Examples of design thinking success
Design thinking has been the go to approach for a lot of organisations to stay relevant by solving end users problems. The below examples show how organizations have used design thinking to solve user’s problems and innovate and create value to their users which shows the benefit of the approach to drive growth and transformation across various industries and domains:
- Airbnb: Airbnb used design thinking to understand their hosts and guests with founders spending time with them. They realized the poor quality photos were affecting the business. They decided to test professional services for hosts that lead to significant increase in bookings. This helped them fight stagnant growth in its early years and scale rapidly into a global hospitality leader
- IBM: IBM used design thinking to shift towards faster development cycles. By embedding design principles into its culture they increased customer satisfaction and created innovative products such as AI powered platform watson
- Bank of America (Keep the Change): Keep the change program of BOA was a result of design thinking which rounds up every purchase to the nearest dollar and deposits the change to a savings account. This initiative came from understanding customers’ challenges in saving money. This program became immensely popular and attracted millions of new customers and increased deposits significantly
- PepsiCo (Design-Led Innovation): CEO Indra Nooyi initiated a design led innovation approach to transform their product development processes. They wanted to bring in consumer experience and empathy in their processes. Which in turn resulted in successful products like new healthy snack lines and more sustainable packaging. Thus resulting in growth in revenue and stronger brand loyalty
- Singapore’s Public Sector: Singapore entirely redesigned their public services to be more user friendly and efficient. They engaged citizens to understand their experiences, pain points and revamped their healthcare, transportation and digital services processes. This helped them with increased citizen satisfaction and reduced cost. This is an applied design thinking principles examples in public sector
How to Apply a Design Thinking Framework to your work?
The first vital thing to apply design thinking is to promote and embrace the design thinking principles and adopt a mindset and process that prioritises understanding user needs and iterative problem solving. The next vital thing is to foster an environment where people collaboratively take decisions and learn from their mistakes and pivot. Teams should openly share their ideas and have a bias towards acting. Here is how a team can apply design thinking framework:

- Empathize with Your Users: It is vital to understand the challenges, needs, goals and behavior of your target users. This can be done by conducting surveys, interviews, observing them in the act or even with empathy maps. Start by deeply understanding the user’s problem and gather insights that help teams to build solutions that really matter and are relevant to the users.
- Define the Problem: Analyse your problems and insights gathered and use fish bone analysis and other techniques to clearly define the specific problem statements that you need to solve. These problem statements should be end user focussed and actionable. This ensures that the entire team is focussed and can brainstorm possible solutions and bring the entire team to a common understanding
- Ideate Creative Solutions: Once the problem statement is written, conduct brainstorming sessions and encourage teams to come up with multiple solutions from different perspectives. You can use mind mapping, role playing and sketching to explore multiple ideas
- Prototype Rapidly: Take the best possible solution which looks promising and quickly create a simple version of the solution or a prototype. These can be your wireframes, low code, no code flows, visual designs etc.Simple sketch, digital mockups or any tool which can make ideas tangible so that they can be tested quickly
- Test and Gather Feedback: Take your prototypes to the real end users to get feedback. Observe how they interact and use your prototype and take their opinions and suggestions. This information can be used to analyse what works, what does not work and what can be improved
- Iterate Based on Insights: Refine your ideas and pivot by using the feedback. This may force you to visit previous steps as new ideas or problems may emerge. This iterative process may continue till your solution is best and efficiently meets the user’s needs
- Implement and Reflect: Once the solution has met your target audience needs, this can be now implemented at full scale. After implementation, reflect on the process to identify the lessons learnt and gaps to improve. This cycle promotes continuous improvement and growth
How can consulting firms help to implement a design thinking process?
A consulting firm can play a crucial role in helping organizations implement the Design Thinking process by providing expertise, structured guidance, and a fresh perspective. They help implement design thinking principles into everyday practices and framework. Below are a few ways in which consultants can help teams
- As Is Assessments – Consultants first start with assessing the current culture and mindset of the team members and also understand the gaps and opportunities for improvement. They come with handy techniques and templates to assess the current state
- Creating Awareness – Consultants conduct engaging and practical immersive workshops and training sessions to educate employees on the five stages of Design Thinking — Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test. A business context led customized and immersive Design Thinking training can act as a foundation of knowledge to the employees and plant a sees in their minds to start thinking and practicing them in their daily tasks
- Subject Matter Experts – Having worked with multiple organizations and domain, consulting firms bring vast knowledge and hands-on experience in Design Thinking principles and methodologies, ensuring a smooth transition from traditional problem-solving methods
- Tailoring the Framework – consultants help in identifying key challenges, biases and resistance and opportunities within the organization by conducting assessments, interviews, and observations. This helps in tailoring the Design Thinking approach to fit the organization’s specific needs, ensuring more relevant and impactful solutions
- Recommending the best Tools – Consultants come with handy tools and techniques to ensure the smooth implementation of the framework. They come with templates for steps like empathy mapping, persona identification etc which helps organizations to understand the concepts in depth
- Facilitation, Coaching and Handholding – Consulting firms facilitate cross-functional collaboration by breaking down silos and encouraging diverse teams to work together. They provide tools and frameworks to guide brainstorming, ideation, and rapid prototyping, promoting creativity and experimentation.
- Building internal capabilities – Consulting firms are experts who can train the teams in upskilling with design thinking concepts, best practices, tools etc. They can also create center of excellence teams for various aspects of the framework who can further drive the adoption within the organization
Conclusion
There are several design thinking frameworks that can be implemented within teams and organizations depending on their business and product context. While all the frameworks are unique and contextual, they are built on the design thinking principles. Design thinking principles offer a powerful framework to encourage creativity, collaboration and solve user problems with innovation. By bringing in empathy, an iterative approach and acting on its design thinking principles enables the team to explore new ideas, experiment and learn continuously from the feedback. Leverage Design thinking services from Design thinking consulting orgs like Benzne to pilot and create initial success stories which will help you create the internal buy in and momentum to build a long term Design Thinking based problem solving in your organization.
Design thinking is not just a methodology but a mindset that empowers teams to think creatively and solve problems which matter to the end users. It need not be only for the designers or for a software product, design thinking can be used or implemented across domains, fields or industries where innovative solutions are required to solve a complex problem. With this our blog on “Key Design Thinking Principles For Business Problem Solving” comes to an end and we sincerely hope this helped. Please write to us at consult@benzne.com for any feedback or suggestions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Key Design Thinking Principles
1. Who can use design thinking?
Design thinking is a simple yet powerful way of working that can be used by anyone or any organization, irrespective of the role, industry or domain. Organizations from various industries and public sectors have benefited tremendously from design thinking. It can be used or implemented for anyone looking to solve problems with collaboration and innovate based on feedback from the end users. Confused if you can use Design Thinking for problem solving in your organization? Connect with Benzne’s Design thinking services to explore if there is a relevant use case and how to leverage DT to solve your unique problems.
2. What are the design thinking tools?
Design thinking tools are techniques and methods that help facilitate the creative problem-solving process, ensuring it remains user-centered and effective. Some common tools include
- Empathy Maps: Visual frameworks that help teams capture insights about users’ thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, fostering a deeper understanding of their needs and experiences
- Personas: Fictional characters representing user types, created based on research to guide design decisions and maintain a focus on real user needs.
- Customer Journey Maps: Visual representations of a user’s experience with a product or service, highlighting pain points and opportunities for improvement
- Brainstorming Sessions: Group activities that encourage idea generation, fostering creativity and diverse thinking
- Prototyping: Creating low-fidelity models or mockups to visualize and test ideas quickly
- User Testing: Gathering feedback from real users to refine and iterate on solutions
3. Is design thinking based on the principle of empathy?
Yes, one the most prominent key principles of design thinking is empathy. In fact the first stage of design thinking is to empathize with the users. Understanding the pain points, challenges, goals, and emotions of the users and then solving their problems proves to be the best way to help end users. By putting yourself in their shoes, you can identify problems and areas of improvement with more precision and solve problems which actually matter.
4. What is the biggest obstacle to design thinking?
Resistance to change is the biggest obstacle for design thinking. With legacy practices, fear of change, ghost of the past with iterative processes, fear of loss of power etc teams and individuals may not like the change in culture of processes. Also, design thinking needs time and resources for activities such as prototyping, research and testing which can also be seen as a barrier.
5. Is design thinking applicable to all problems?
Design thinking helps foster creativity and solve user’s problems with experimentation. While it is a powerful approach to solve complex problems, its effectiveness depends on the nature of the problem. It is mostly effective where user needs and experiences are vital like product design, service improvements.

